
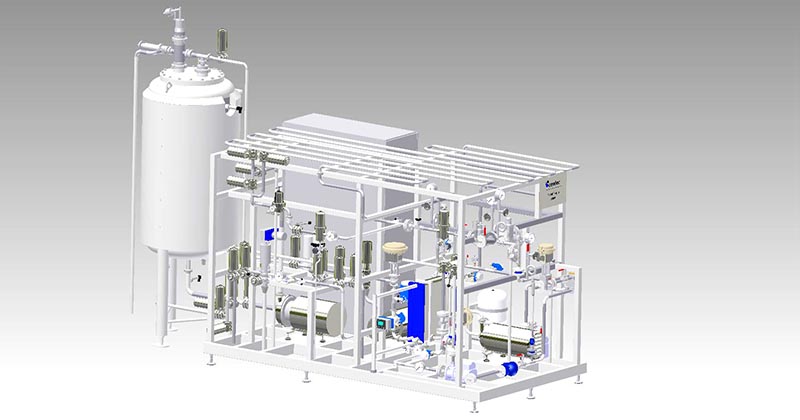
Yeast Thermolizer
Application
The Yeast Thermolizer deactivates yeast by pasteurization. Containing a high level of vitamin B and proteins, waste or surplus yeast is a valuable product which can be used after thermalization.
Description
For thermal deactivation the yeast is heated to its deactivation temperature. The yeast flows through a special heat exchanger, then into a holding tube. Hot water or steam can be used as heating medium. In the holding tube the yeast is held at the deactivation temperature for a specified time. Typically, 10 seconds at 75 °C is sufficient to deactivate yeast. In this way, all the live cell membranes are ruptured. For efficient energy use, the deactivation system can be designed as a two-stage system with a regeneration zone. The first step is energy recovery. The live yeast is heated as it flows in counter current to already deactivated hot yeast. Heat from the deactivated yeast is thereby returned to the process. In the second step the yeast is warmed up to the target deactivation temperature by the heating medium.
- Constant deactivation, with highly accurate process control
- Heat recovery for efficient energy use and minimized operating costs
- Customized modular design with a standard PLC
- Skid mounted for easy installation and start-up
- Hygienic execution and full CIP capability
Typical Technical Data
| Capacity | 10 - 1.000 hl/h |
| Deactivation Temperature/Holding Time | depending on product/application |
| Material | according to requirements (1.4301/AISI 304, 1.4404/AISI 316L, …) |
| Heating Medium | hot water, steam (primary source) |
| Cooling Medium | glycol, ice water, ammonia, brine |
| Options | different automation levels; remote maintenance access; heat recovery section; booster pump; cooling |






 Mr. Hà
Mr. Hà live:ha_1652
live:ha_1652






















